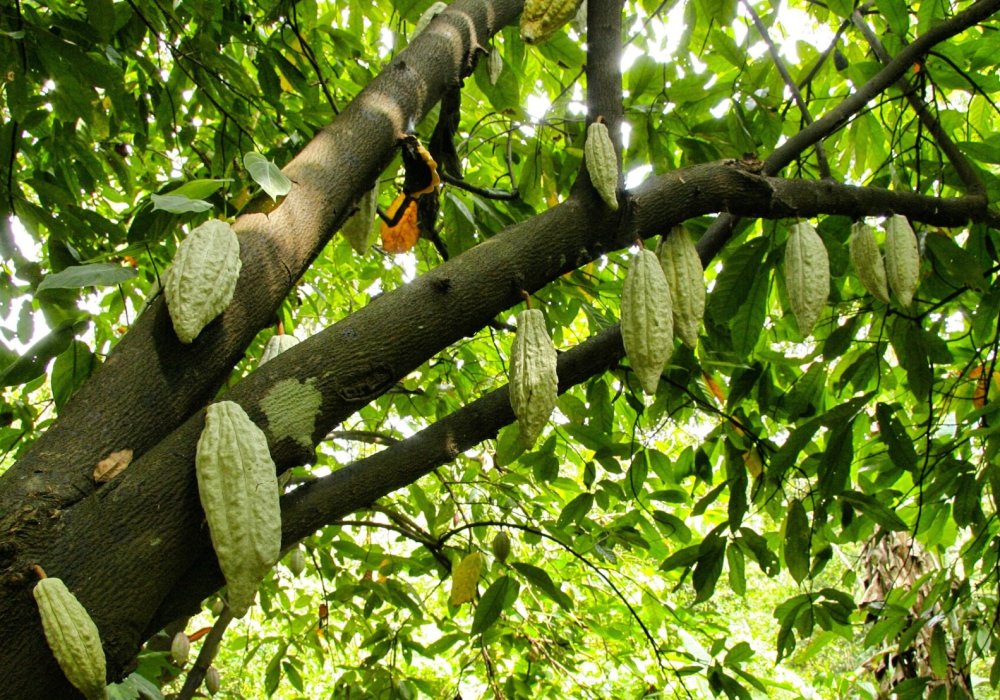
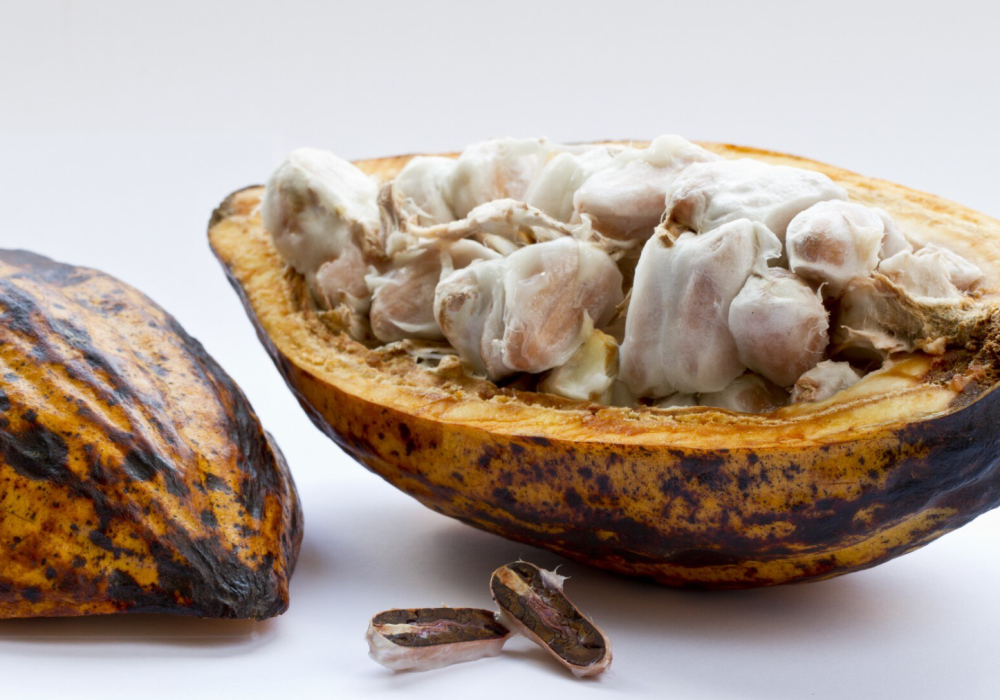



balanced acidity, and long-lasting
finish—flavor characteristics shaped by a uniquely tropical climate.



The Taste of the Soil. The Scent of the Wind. The Story of Vietnam
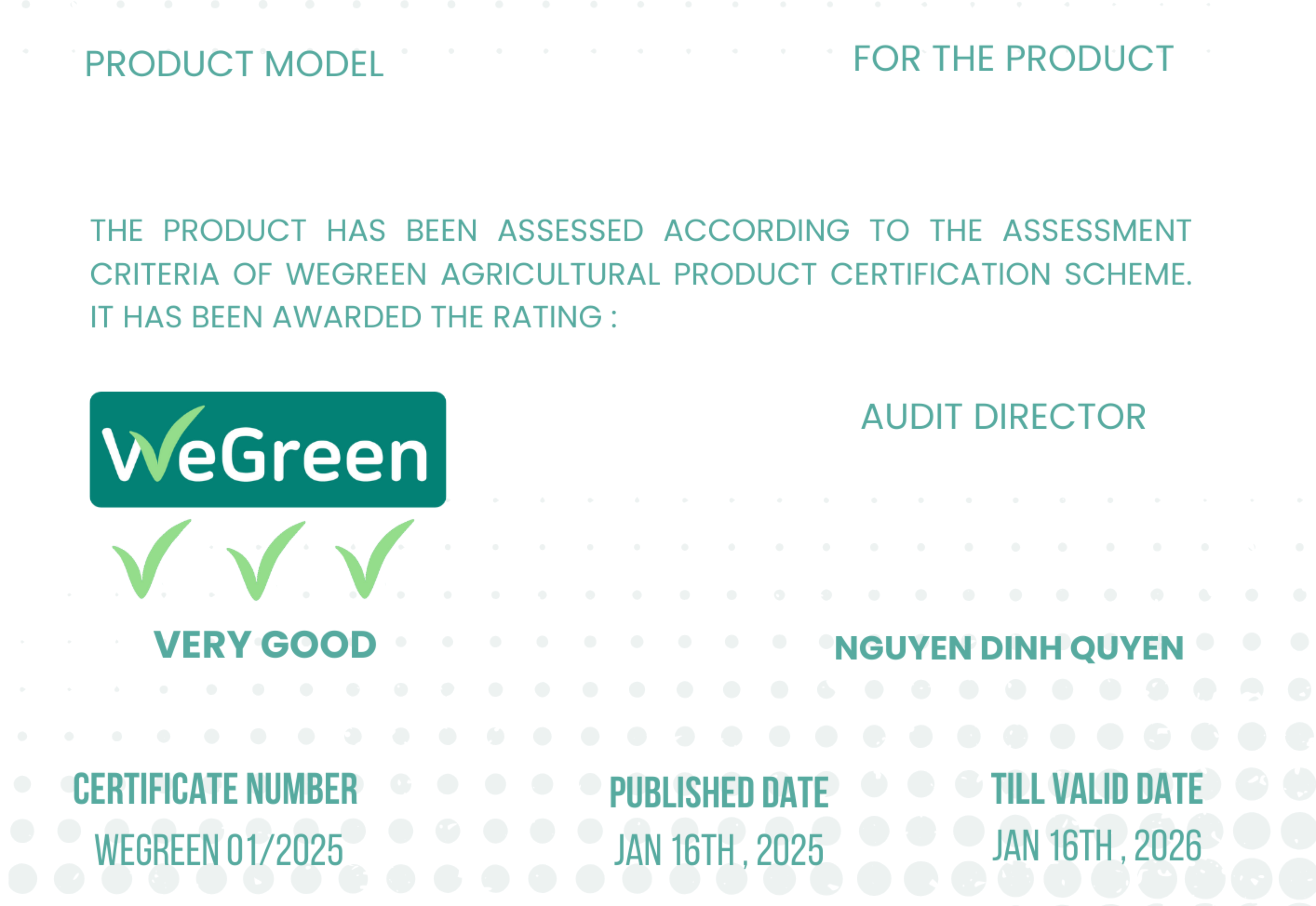
Methodology for Sustainable Production Practices under the WeGreen Certification
The methodology for sustainable production practices under the WeGreen certification is a comprehensive approach designed to optimize the use of natural resources, minimize negative environmental impacts, and ensure economic and social benefits for all stakeholders.
This methodology is typically based on international principles and standards, integrating scientific, technological, and management components to guide sustainable and responsible production.
Key Pillars of the Methodology
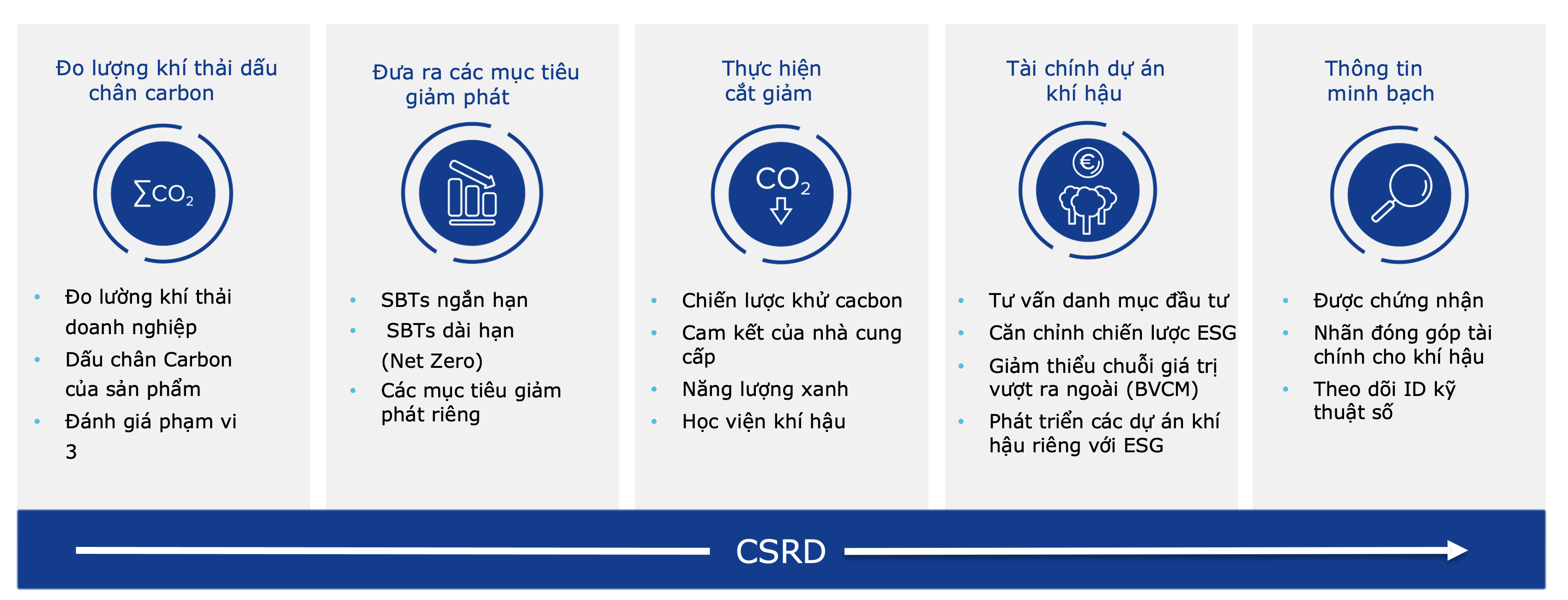
1. The methodology for sustainable production practices is typically built on three main pillars:
a. Environmental
- Efficient resource use: Optimize the use of water, energy, and input materials while minimizing waste.
- Resource conservation and regeneration: Apply techniques such as recycling, reuse, and circular production to protect natural resources.
- Emission reduction: Reduce greenhouse gases, toxic chemicals, and other pollutants through clean technologies and improved production processes.
b. Economic
- Enhanced production efficiency: Utilize modern technologies to reduce costs, increase productivity, and improve product quality.
- Long-term value creation: Develop sustainable products with high market value that meet growing demand for responsible and eco-friendly goods.
- Increased competitiveness: Meeting sustainability standards helps businesses gain an advantage in international markets.
c. Social
- Improved working conditions: Ensure occupational safety, fair wages, and better working environments for employees.
- Community development: Support local communities through education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
- Promotion of social responsibility: Prevent child labor, discrimination, and human rights violations across the supply chain.
2. The process for implementing sustainable production practices
Step 1: Baseline assessment
- Analyze current production processes to identify levels of resource consumption, emissions, and other environmental impacts.
- Evaluate risks within the supply chain, including economic and social factors.
Step 2: Strategic planning
- Define short-term and long-term sustainability goals based on international standards such as ISO 14001, GRI, or ESG commitments.
- Develop a detailed action plan to address each aspect: environmental, economic, and social.
Step 3: Adoption of technologies and improved processes
- Implement clean production technologies such as renewable energy, smart automation, and circular production systems.
- Use environmentally friendly materials and minimize waste throughout the entire supply chain.
Step 4: Training and awareness-building
- Organize training programs for workers and stakeholders to help them understand sustainability standards and best practices.
- Build a sustainability-focused culture within the organization, encouraging innovation and continuous improvement.
Step 5: Monitoring and evaluation
- Use tools and tracking systems to measure sustainability performance (e.g., energy consumption, carbon emissions, product quality).
- Conduct periodic assessments and adjust strategies to ensure goals are achieved.
3. Key performance evaluation criteria
Sustainable production performance is assessed based on:
- Environmental: Reduced emissions, wastewater, and solid waste; increased recycling and reuse.
- Economic: Higher profits, lower production costs, and expanded market reach.
- Social: Improved livelihoods for workers and communities, protected rights, and enhanced working conditions.
4. Benefits of the sustainable production methodology
- Environmental protection: Minimized negative impacts on ecosystems and improved resource conservation.
- Enhanced competitive advantage: Sustainable products are increasingly preferred by consumers, especially in developed markets.
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting environmental and labor requirements helps businesses avoid legal risks.
- Brand reputation building: Companies practicing sustainable production are highly regarded and trusted by partners and customers.

